Sanctuary Boundaries
Overview
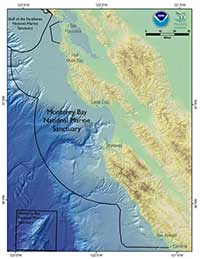 Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary (MBNMS) is the largest marine sanctuary in the United States, covering 6,094 square statute miles (4,601 nmi2) of California ocean waters from Cambria to the Marin Headlands. The seafloor within the sanctuary reaches a depth of 12,743 feet (2.4 miles) below the ocean surface.
Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary (MBNMS) is the largest marine sanctuary in the United States, covering 6,094 square statute miles (4,601 nmi2) of California ocean waters from Cambria to the Marin Headlands. The seafloor within the sanctuary reaches a depth of 12,743 feet (2.4 miles) below the ocean surface.
The marine sanctuary encompasses no dry ground. Its shoreward boundary extends inland no further than the mean high tide line. Inner harbor areas are excluded from sanctuary boundaries. The only inland waterway included in the sanctuary is the main channel of Elkhorn Slough east from the Highway 1 bridge to the Elkhorn Road tide gates.
MBNMS boundaries are defined in Title15 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Section 922.130.
Federal protection of the sanctuary's natural resources is three-dimensional, protecting the submerged lands below, the water column, the water surface, and all habitat and wildlife throughout its boundaries.
MBNMS offers various free sanctuary boundary maps for download.
